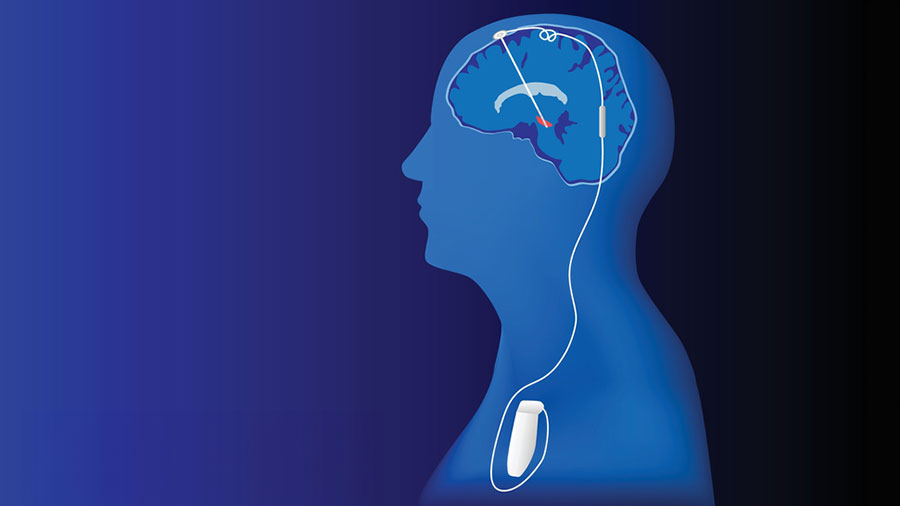
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is an effective surgical procedure used in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. This method aims to regulate the activity of the nervous system by sending regular electrical stimuli through electrodes implanted into the brain. It is often a preferred option for treating various conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Conditions Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical method used in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric disorders. To understand the use of Deep Brain Stimulation for specific conditions, let’s detail some particular cases:
Parkinson’s Disease:
DBS is frequently used to control motor symptoms, particularly in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. These symptoms include tremors, rigidity, and movement disorders. If symptoms cannot be adequately controlled with medication or if the side effects of drugs are intolerable, DBS may be considered, especially in advanced stages of Parkinson’s or when the effectiveness of drug treatments diminishes over time.
Essential Tremor:
Essential tremor is a condition characterized by involuntary shaking or trembling in the hands. DBS can be an effective option to control essential tremor, especially when medication treatments are ineffective or problematic in terms of side effects.
Dystonia:
Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by muscle spasms and involuntary muscle contractions. DBS may show positive results in regulating dystonic movements when medication treatments are ineffective or side effects are intolerable.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
DBS can be used to alleviate symptoms in individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder, especially when other treatment options have failed or proved ineffective. DBS may be considered when specific aspects of OCD significantly impact daily life and substantially reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Deep Brain Stimulation, when used for these specific conditions, requires an individual assessment based on the effectiveness of the treatment, the patient’s overall health, and the severity of symptoms. Each patient is unique, so the decision regarding treatment should be made by a specialist neurologist or neurosurgeon.
When Should Deep Brain Stimulation (Brain Pacemaker) Be Applied?
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is an effective surgical procedure in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders and is considered in specific cases. The application process of DBS includes a personalized approach focusing on the individual needs and treatment goals of patients. Here are the details of the Deep Brain Stimulation application process:
Inadequate Response to Medication Treatments:
Deep Brain Stimulation is often considered when conditions cannot be adequately controlled with medication treatments. Especially in neurological disorders like Parkinson’s, the effectiveness of drugs may decrease over time, and DBS can help in more effectively controlling symptoms.
Symptoms Negatively Impacting Daily Life:
DBS may be considered when neurological or psychiatric symptoms significantly affect daily life activities. For instance, movement disorders in Parkinson’s disease or compelling thoughts and behaviors in obsessive-compulsive disorder can seriously diminish a person’s quality of life. In such cases, DBS may offer a solution to better control symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Failure of Other Treatment Methods:
Deep Brain Stimulation is considered when other treatment options have failed or are not suitable. If drug treatments or other surgical interventions have not produced the desired results or if the side effects are intolerable, DBS may be an alternative.
Presence of Specific Neurological or Psychiatric Disorders:
DBS is particularly used in the treatment of specific neurological and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The symptoms of these disorders play a crucial role in determining the appropriateness of DBS.
General Health and Tolerance to Surgery:
DBS surgery is typically performed on patients with good overall health who can tolerate the surgical intervention. For patients with health conditions that may not tolerate the surgery well, DBS is evaluated, taking into account the risks and benefits.
Deep Brain Stimulation is assessed by a multidisciplinary health team based on these criteria, creating a personalized treatment plan tailored to the individual needs and symptoms. This assessment involves interaction with the patient and their family, and the treatment decision is made by a specialist neurologist or neurosurgeon.
How Is Deep Brain Stimulation Applied?
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is an effective surgical method in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. This method aims to regulate neural activity by sending regular electrical stimuli to the brain through electrodes implanted into the brain. The application process of Deep Brain Stimulation consists of the following stages:
Patient Assessment and Selection:
Before the application of Deep Brain Stimulation, a detailed evaluation of the patient’s general health, symptoms, and treatment history is conducted. During this assessment, it is determined whether the patient is suitable for surgery. Specialists evaluate the potential benefits of DBS to improve the patient’s symptoms and quality of life.
Surgical Planning:
After identifying suitable candidates, surgeons create a surgical plan. This planning includes determining specific areas where electrodes will be placed. The planning is customized based on the patient’s individual condition and treatment goals.
Surgery Day:
DBS surgery typically occurs in two stages. The first stage is often performed with the patient consciously awake. Surgeons monitor the patient’s brain activities in real-time to accurately place the electrodes in the correct regions. The second stage involves the placement of the generator (brain pacemaker) beneath the skin, usually performed a few days later through a separate surgical procedure.
Electrode Placement:
The surgical team precisely places the electrodes into the target regions of the brain. During this process, the patient’s brain activities and reactions are continuously monitored. Accurate placement of the electrodes is crucial for the effectiveness of the treatment.
Placement of the Generator (Brain Pacemaker) Device:
Once the electrodes are placed, a generator (brain pacemaker) is implanted beneath the skin. This device receives signals from the electrodes and controls the regular electrical stimuli applied to the brain.
Programming and Settings:
After surgery, experts program the device. The settings of the electrodes and the generator are personalized based on the patient’s symptoms and response. This process is a meticulous one where experts work to achieve the best clinical response for the patient.
The recovery process and effectiveness of treatment are regularly monitored after Deep Brain Stimulation surgery. This process involves continuous communication between the patient and the healthcare team, and the treatment plan is revised if necessary. Deep Brain Stimulation plays a significant role as a reliable treatment option in the management of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s Disease Treatment: Who Are the Candidates?
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder characterized by the loss of cells producing dopamine in the brain. This disease typically manifests with symptoms such as tremors, muscle stiffness, slowed movement, and balance problems. In advanced stages, the effectiveness of drug treatments may diminish, or their side effects may become intolerable. At this point, deep brain stimulation (DBS) or brain pacemaker surgery may be considered for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. So, who are the candidates for brain pacemaker surgery in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease?
Those Whose Symptoms Cannot Be Controlled with Medications:
Drugs commonly used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease can often control symptoms. However, in advanced cases, the effectiveness of medications may decrease or prove insufficient. Brain pacemaker surgery may be considered when drug treatments are ineffective.
Those Experiencing Intolerable Side Effects of Medications:
The side effects of certain Parkinson’s medications can be intolerable for some patients. Particularly in cases where the quality of life has decreased due to medication side effects, brain pacemaker surgery may be considered.
Those with Motor Complications:
In the advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease, motor complications may arise in patients. These complications may include “waving” movements (dyskinesias) and noticeable difficulty in movement during times when medications are ineffective. Brain pacemaker surgery could be an option for controlling symptoms in individuals with such motor complications.
Those Whose Appropriate Brain Areas Can Be Identified:
Brain pacemaker surgery involves placing electrodes in specific brain regions. Therefore, it is crucial that suitable brain areas can be identified before the surgery. Candidates who can have electrodes accurately placed in appropriate brain areas may be considered suitable for brain pacemaker surgery.
Patient and Family Consent and Collaboration:
Because brain pacemaker surgery is a significant surgical intervention, full consent and collaboration from the patient and their family are essential for evaluating and implementing this treatment option. The risks and benefits of the surgery should be explained in detail, and the patient’s decision should be shaped in light of this information.
Brain pacemaker surgery should be considered as an alternative in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, but each patient is unique. Therefore, the treatment decision should be made by a multidisciplinary healthcare team, typically consisting of neurologists, neurosurgeons, psychiatrists, and rehabilitation experts. Brain pacemaker surgery can play a significant role in controlling symptoms and improving the quality of life for eligible candidates.
Deep Brain Stimulation in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive loss of cognitive functions, typically occurring with age. Currently, there is no fully effective method for treating Alzheimer’s disease, but research on surgical treatment options for neurological disorders, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS), shows promising results.
The Role of DBS in Alzheimer’s Treatment:
In recent years, there has been an increase in research examining the effects of DBS on Alzheimer’s disease. The potential benefits of DBS may include:
Regulating Brain Activity: DBS can regulate neural activity by sending regular signals to specific brain regions. Since Alzheimer’s disease causes neuronal loss in specific areas, increasing activity in these regions may contribute to improvement in memory and cognitive functions.
Influencing Neurotransmitter Levels: One potential mechanism of DBS in Alzheimer’s treatment is its ability to influence neurotransmitter levels in the brain, regulating neural transmission. Increasing depleted acetylcholine levels, especially in Alzheimer’s disease, may have positive effects on cognitive functions.
Improving Cognitive Functions: Some studies suggest that DBS may improve cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s patients. Potential increases in memory, attention, and other cognitive abilities make DBS a consideration for Alzheimer’s treatment.
However, the role of DBS in Alzheimer’s treatment is not fully understood, and research is ongoing. Comprehensive clinical trials are needed to gather more information on the effectiveness, reliability, and long-term outcomes of the treatment. Therefore, advanced research is necessary to form a clear opinion on whether DBS is a definitive solution for Alzheimer’s treatment.
December 25, 2023 9:00 am

