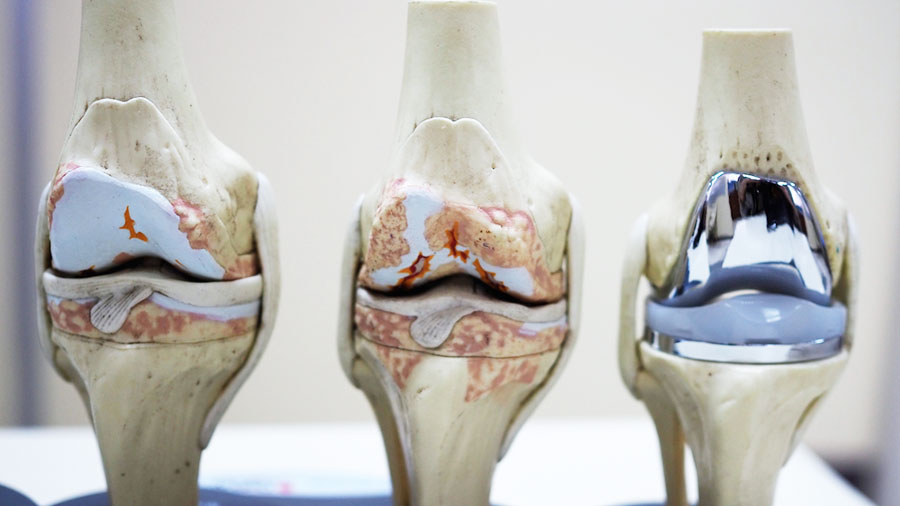
Today, knee problems rank among common health issues stemming from factors like aging, injuries, or degenerative diseases. Knee replacement surgery has become a significant option to address these conditions and enhance patients’ quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the topic of “Knee Replacement Surgery” in detail, focusing on a range of important issues from the advantages of the surgery to post-operative care.
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is performed to treat damaged tissues or degenerative changes in the knee joint. This surgical intervention is typically carried out using prosthetic implants. The surgery is a preferred method for patients aiming to reduce pain, regain mobility, and improve their quality of life.
Why is Knee Replacement Necessary? When is it Preferred?
Knee replacement, a surgical treatment method, is typically used to replace damaged or degenerative tissues in the knee joint that cause pain and limited mobility. Osteoarthritis is one of the most common reasons for surgery. The following are situations where surgery may be necessary:
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis, resulting from the wear and degeneration of cartilage tissue in the knee joint, is one of the most common reasons for knee replacement surgery. This condition can occur due to factors such as aging, overuse, genetic factors, or traumatic injuries.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints by targeting the immune system. In cases of joint damage, knee replacement surgery may be considered.
- Traumatic Injuries: Severe injuries, fractures, or ligament damage in the knee can lead to permanent damage to joint tissues. In such cases, knee replacement surgery may be an option for repairing or replacing damaged tissues.
- Inflammatory Arthritis: Inflammatory conditions in the knee joint, such as ankylosing spondylitis or other types of inflammatory arthritis, may necessitate knee replacement.
- Genetic and Congenital Anomalies: Some genetic factors or congenital disorders can hinder the normal development of the knee joint, leading to damage over time.
- Knee Osteoarthritis: Calcification of cartilage tissue in the knee joint can cause pain and limited mobility. Knee replacement surgery may be considered if osteoarthritis progresses.
- Chronic Pain and Mobility Limitations: Chronic knee pain, mobility limitations, and difficulties in performing daily activities may indicate the necessity of knee replacement surgery.
Knee Prosthetic Implants
Knee prosthetic implants are typically made from biocompatible materials such as titanium and polyethylene. These implants are designed to provide movement similar to that of a natural knee joint.
What are Total Knee Prostheses and Partial Knee Prostheses?
Total knee prosthesis is a procedure in which all damaged tissues and bones on the knee joint are replaced. Partial knee prosthesis, on the other hand, is a procedure in which only damaged tissues in a specific area are replaced.
What is Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery?
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the use of robotic surgical techniques in knee replacement surgery. Robotic surgery can enhance the success rate of the surgery by providing a more precise and personalized surgical experience.
Knee Prosthesis Procedure
The knee prosthesis procedure typically lasts 1 to 2 hours and involves the following steps:
1. Pre-evaluation: Before deciding on knee replacement surgery, a detailed pre-evaluation is conducted between the patient and the doctor. The patient’s overall health, medical history, complaints, and lifestyle are assessed. If necessary, the condition of the knee is examined using X-rays, MRI, or other imaging techniques.
2. Preoperative Preparation: During the preoperative process, the patient discusses surgery details and expectations with the surgical team. The patient may undergo a series of tests before surgery and is instructed to follow the doctor’s recommended guidelines.
3. Anesthesia: Knee replacement surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, allowing the patient to sleep during the procedure and feel no pain or discomfort.
4. Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the front of the knee and pulls the muscles aside to access the joint. The incision is usually made using minimally invasive techniques, speeding up the healing process.
5. Removal of Damaged Tissues: The surgeon removes damaged or degenerative tissues from the knee joint to create the necessary space for opening the joint and placing the prosthetic implant.
6. Placement of Prosthetic Implant: The prosthetic implant, which is of appropriate size and shape, is inserted to replace the removed damaged tissues. These implants are typically made of titanium or ceramic materials and aim to mimic natural joint movement.
7. Stitching and Closure: After placing the prosthetic implant, the surgeon closes the incision and stitches it. The incision is usually made in an aesthetically pleasing manner and aimed at minimizing the healing process.
8. Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation: During the postoperative period, the patient may stay in the hospital for several days. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are applied to help the patient regain joint movement and muscle strength. Additionally, medications such as pain relievers and antibiotics recommended by the doctor may be used.
9. Follow-up Checks: It is important for the patient to regularly attend follow-up appointments with the doctor during the postoperative period. During these check-ups, the healing of the surgical area and the condition of the prosthetic implant are evaluated.
Complications and Risks of Knee Arthroplasty
Like any surgical procedure, knee arthroplasty carries certain risks. Complications may include infection, blood clots, implant problems, and nerve damage. However, with surgeries performed by expert surgeons and careful postoperative follow-up, these risks can be minimized.
Postoperative Care for Knee Arthroplasty
Effective care following knee prosthetic surgery is critical for a successful recovery process. Postoperative care involves steps such as regularly using prescribed medications, attending physical therapy sessions, and adhering to the designated rehabilitation protocol.
Recovery Time for Knee Prosthesis
The recovery period for knee prosthesis varies depending on factors such as the patient’s overall health, age, preoperative condition, and the complexity of the surgical intervention. For instance, partial knee replacement typically has a shorter recovery time compared to total knee replacement. However, generally, patients can return to their daily activities within a few weeks after surgery. Full recovery may take several months. Compliance with the doctor’s instructions ensures a successful recovery process.
What to Consider After Knee Prosthesis Surgery?
- Be diligent in following your doctor’s and physiotherapist’s instructions.
- Avoid excessive exercise and lifting heavy weights.
- Avoid sitting with your legs crossed for the first 6 weeks.
- Ensure to take the prescribed medications.
- Do not skip your follow-up appointments.
- Do not kneel, squat, or bend your knee until approved by your doctor.
- Take short walks as advised by your doctor to prevent clotting.
- Avoid prolonged standing.
Rehabilitation Protocol for Knee Arthroplasty
Rehabilitation is a crucial process aimed at facilitating the patient’s return to normal daily life following knee prosthetic surgery. Exercises guided by physiotherapists enhance range of motion and strengthen muscles, expediting the patient’s recovery process. However, there are exercises to be avoided after knee replacement. Overly strenuous or incorrectly performed exercises may adversely affect the recovery process. Therefore, starting exercise programs without physiotherapist recommendation should be avoided.
Permanent Limitations After Knee Prosthesis
Following knee prosthetic surgery, most patients typically lead a more active life with reduced pain. However, as with any surgical intervention, some permanent limitations may arise in certain cases. These limitations may vary depending on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the surgical intervention, and compliance with the recovery process. Some of these limitations include:
Activities Putting Excessive Strain on the Knee Joint
Activities such as excessive running and walking on hard surfaces can shorten the lifespan of the prosthesis or cause damage to the implant. Additionally, high-impact sports like running, football, and basketball can reduce the durability of the prosthetic implant and lead to wear and tear. Avoiding activities that apply excessive pressure to the knee joint or may cause imbalance is important for ensuring the safety and durability of the prosthetic implant.
High-Risk Sports
After knee replacement surgery, it is important for patients to avoid engaging in high-risk sports and activities. These activities include high-impact and high-risk sports such as mountaineering, diving, and karate.
Sedentary Lifestyle and Related Weight Gain
Excess weight puts extra strain on the prosthetic implant and can reduce its durability. Maintaining a healthy weight management regimen will support the long-term success of the implant.
After knee replacement surgery, patients are encouraged to maintain an active lifestyle. However, these activities should be safe and low-risk. Low-impact sports such as swimming, walking, and cycling are generally more suitable for individuals with knee prostheses.
Joint Flexibility and Range of Motion
Following surgery, while joint flexibility and range of motion may improve, some patients may not regain full normal mobility. However, this varies from person to person.
Limitations Based on Age and Overall Health
The patient’s age and overall health can influence the recovery process. In elderly patients, the full recovery process may take longer, and some limitations may be more pronounced.
Advantages of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery offers numerous advantages. These include reduced pain, increased mobility, and expedited return to daily life activities. The long-term benefits of the surgery enable patients to lead healthier and more active lives.
Disadvantages of Knee Replacement Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, knee replacement surgery also comes with certain disadvantages. These may include the risk of infection, implant issues, and a prolonged recovery process. When considering knee replacement surgery, it is essential to weigh these disadvantages alongside the advantages and your individual circumstances. Before making a surgical decision, it is important to have a detailed discussion with your doctor and understand the expectations before and after the surgery.
Cost of Knee Replacement Surgery
The cost of knee replacement surgery varies depending on the type of implant used, the location of the hospital, and the experience of the surgical team. Patients should seek detailed information about this before the surgery and evaluate their insurance coverage. Moreover, in Turkey, the costs of knee replacement are generally lower compared to Western countries.
Alternatives to Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery can be an effective solution for many patients with knee problems. However, in some cases, alternative treatments should be considered before surgical intervention is recommended. These alternatives may include medication therapy, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. These options should be evaluated by expert doctors depending on the patients’ condition.
In summary, alternatives to knee replacement can include:
- Weight loss and supportive lifestyle changes to reduce the load on the knees in cases of obesity.
- Strengthening knee muscles with light exercises such as swimming, walking, and cycling.
- Use of pain-relieving medications.
- Intra-articular steroid injections.
- Different surgical techniques such as arthroscopy, osteotomy, and microfracture technique.
The above alternative methods may not be suitable or sufficient for everyone. Therefore, consulting with a specialist doctor is important to determine the most appropriate treatment method.
Knee replacement surgery provides a significant solution for individuals experiencing knee problems. However, it is important for patients to have detailed discussions with their doctors when making this decision, clarifying their expectations before and after the surgery. This way, doors to a healthy and active life can be opened, relieving pain, and enjoying daily activities. Remember, investing in your health is the first step towards improving your quality of life!
Frequently Asked Questions
Knee replacement surgery typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. However, the duration may vary depending on the complexity of the surgery and the patient’s overall health condition.
The recovery time for knee replacement varies from person to person but generally ranges between 6 weeks to 3 months. The full recovery process may take longer, depending on regular follow-up with physical therapy and rehabilitation.
Yes, many patients can return to normal life after knee replacement surgery. Pain decreases, mobility improves, and daily activities can be performed more comfortably.
Usually, after knee replacement surgery, patients should avoid heavy lifting and high-impact sports. However, this requires a personalized assessment.
Since anesthesia is typically administered during surgery, patients do not feel pain. Pain can be managed postoperatively using minimal pain control methods.
Patients usually start walking shortly after knee replacement surgery. However, the full recovery process and complete walking ability may take several weeks.
The hardest day is typically the first few days after surgery when pain and discomfort are felt. However, this process improves over time.
Knee replacement surgery is generally performed on middle-aged and older patients. However, it can be performed at any age based on overall health condition and symptoms.
Usually, the ability to squat is regained after knee replacement surgery, but it should be performed in accordance with your doctor’s recommendations and physical therapy program.
Yes, the ability to climb stairs is usually regained after knee replacement surgery as part of the recovery process supported by physical therapy.
The fastest way to recover from knee replacement surgery is through regular physical therapy, consistent medication use, healthy eating, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and full compliance with doctor’s instructions.
The hardest part is often the pain and discomfort felt in the early stages of the recovery process, along with the challenges of rehabilitation and physical limitations.


